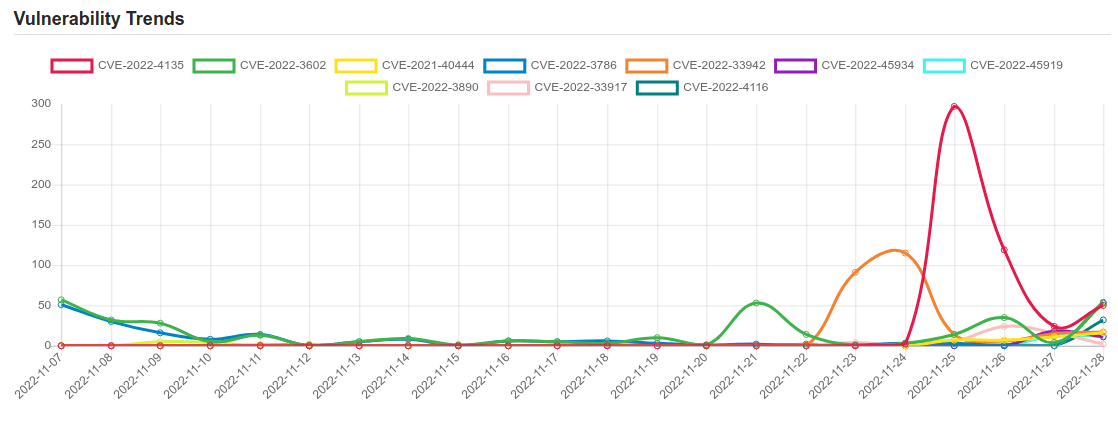
Daily Vulnerability Trends: Tue Nov 29 2022
| CVE NAME | CVE Description |
| CVE-2022-40684 | An authentication bypass using an alternate path or channel [CWE-288] in Fortinet FortiOS version 7.2.0 through 7.2.1 and 7.0.0 through 7.0.6, FortiProxy version 7.2.0 and version 7.0.0 through 7.0.6 and FortiSwitchManager version 7.2.0 and 7.0.0 allows an unauthenticated atttacker to perform operations on the administrative interface via specially crafted HTTP or HTTPS requests. |
| CVE-2022-45933 | KubeView through 0.1.31 allows attackers to obtain control of a Kubernetes cluster because api/scrape/kube-system does not require authentication, and retrieves certificate files that can be used for authentication as kube-admin. NOTE: the vendor’s position is that KubeView was a “fun side project and a learning exercise,” and not “very secure.” |
| CVE-2022-45930 | A SQL injection issue was discovered in AAA in OpenDaylight (ODL) before 0.16.5. The aaa-idm-store-h2/src/main/java/org/opendaylight/aaa/datastore/h2/DomainStore.java deleteDomain function is affected for the /auth/v1/domains/ API interface. |
| CVE-2022-40127 | A vulnerability in Example Dags of Apache Airflow allows an attacker with UI access who can trigger DAGs, to execute arbitrary commands via manually provided run_id parameter. This issue affects Apache Airflow Apache Airflow versions prior to 2.4.0. |
| CVE-2022-33679 | Windows Kerberos Elevation of Privilege Vulnerability. This CVE ID is unique from CVE-2022-33647. |
| CVE-2022-34721 | Windows Internet Key Exchange (IKE) Protocol Extensions Remote Code Execution Vulnerability. This CVE ID is unique from CVE-2022-34722. |
| CVE-2022-43705 | In Botan before 2.19.3, it is possible to forge OCSP responses due to a certificate verification error. This issue was introduced in Botan 1.11.34 (November 2016). |
| CVE-2022-45931 | A SQL injection issue was discovered in AAA in OpenDaylight (ODL) before 0.16.5. The aaa-idm-store-h2/src/main/java/org/opendaylight/aaa/datastore/h2/UserStore.java deleteUser function is affected when the API interface /auth/v1/users/ is used. |
| CVE-2022-3602 | A buffer overrun can be triggered in X.509 certificate verification, specifically in name constraint checking. Note that this occurs after certificate chain signature verification and requires either a CA to have signed the malicious certificate or for the application to continue certificate verification despite failure to construct a path to a trusted issuer. An attacker can craft a malicious email address to overflow four attacker-controlled bytes on the stack. This buffer overflow could result in a crash (causing a denial of service) or potentially remote code execution. Many platforms implement stack overflow protections which would mitigate against the risk of remote code execution. The risk may be further mitigated based on stack layout for any given platform/compiler. Pre-announcements of CVE-2022-3602 described this issue as CRITICAL. Further analysis based on some of the mitigating factors described above have led this to be downgraded to HIGH. Users are still encouraged to upgrade to a new version as soon as possible. In a TLS client, this can be triggered by connecting to a malicious server. In a TLS server, this can be triggered if the server requests client authentication and a malicious client connects. Fixed in OpenSSL 3.0.7 (Affected 3.0.0,3.0.1,3.0.2,3.0.3,3.0.4,3.0.5,3.0.6). |
| CVE-2021-40444 | Microsoft MSHTML Remote Code Execution Vulnerability |
| CVE-2022-3786 | A buffer overrun can be triggered in X.509 certificate verification, specifically in name constraint checking. Note that this occurs after certificate chain signature verification and requires either a CA to have signed a malicious certificate or for an application to continue certificate verification despite failure to construct a path to a trusted issuer. An attacker can craft a malicious email address in a certificate to overflow an arbitrary number of bytes containing the `.’ character (decimal 46) on the stack. This buffer overflow could result in a crash (causing a denial of service). In a TLS client, this can be triggered by connecting to a malicious server. In a TLS server, this can be triggered if the server requests client authentication and a malicious client connects. |
| CVE-2022-33942 | Protection mechanism failure in the Intel(R) DCM software before version 5.0 may allow an unauthenticated user to potentially enable escalation of privilege via adjacent access. |
| CVE-2022-45934 | An issue was discovered in the Linux kernel through 6.0.10. l2cap_config_req in net/bluetooth/l2cap_core.c has an integer wraparound via L2CAP_CONF_REQ packets. |
| CVE-2022-45919 | An issue was discovered in the Linux kernel through 6.0.10. In drivers/media/dvb-core/dvb_ca_en50221.c, a use-after-free can occur is there is a disconnect after an open, because of the lack of a wait_event. |
| CVE-2022-33917 | An issue was discovered in the Arm Mali GPU Kernel Driver (Valhall r29p0 through r38p0). A non-privileged user can make improper GPU processing operations to gain access to already freed memory. |
| CVE-2022-4116 | A vulnerability was found in quarkus. This security flaw happens in Dev UI Config Editor which is vulnerable to drive-by localhost attacks leading to remote code execution. |
| CVE-2022-41924 | A vulnerability identified in the Tailscale Windows client allows a malicious website to reconfigure the Tailscale daemon `tailscaled`, which can then be used to remotely execute code. In the Tailscale Windows client, the local API was bound to a local TCP socket, and communicated with the Windows client GUI in cleartext with no Host header verification. This allowed an attacker-controlled website visited by the node to rebind DNS to an attacker-controlled DNS server, and then make local API requests in the client, including changing the coordination server to an attacker-controlled coordination server. An attacker-controlled coordination server can send malicious URL responses to the client, including pushing executables or installing an SMB share. These allow the attacker to remotely execute code on the node. All Windows clients prior to version v.1.32.3 are affected. If you are running Tailscale on Windows, upgrade to v1.32.3 or later to remediate the issue. |
| CVE-2022-38374 | A improper neutralization of input during web page generation (‘cross-site scripting’) in Fortinet FortiADC 7.0.0 – 7.0.2 and 6.2.0 – 6.2.4 allows an attacker to execute unauthorized code or commands via the URL and User fields observed in the traffic and event logviews. |
| CVE-2022-4135 | Google Chrome buffer overflow | CVE-2022-4135 |
| CVE-2022-3890 | Google Chrome Crashpad code execution | CVE-2022-3890 |
A considerable amount of time and effort goes into maintaining this website, creating backend automation and creating new features and content for you to make actionable intelligence decisions. Everyone that supports the site helps enable new functionality.
If you like the site, please support us on Patreon using the button below

To keep up to date follow us on the below channels.





![Cobalt Strike Beacon Detected - 140[.]143[.]132[.]170:80 9 Cobalt-Strike](https://www.redpacketsecurity.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/11/Cobalt-Strike-300x201.jpg)
