PANO – Advanced OSINT Investigation Platform Combining Graph Visualization, Timeline Analysis, And AI Assistance To Uncover Hidden Connections In Data
PANO is a powerful OSINT investigation platform that combines graph visualization, timeline analysis, and AI-powered tools to help you uncover hidden connections and patterns in your data.
Getting Started
-
Clone the repository:
bash git clone https://github.com/ALW1EZ/PANO.git cd PANO -
Run the application:
- Linux:
./start_pano.sh - Windows:
start_pano.bat
The startup script will automatically: – Check for updates – Set up the Python environment – Install dependencies – Launch PANO
In order to use Email Lookup transform You need to login with GHunt first. After starting the pano via starter scripts;
- Select venv manually
- Linux:
source venv/bin/activate - Windows:
call venv\Scripts\activate - See how to login here
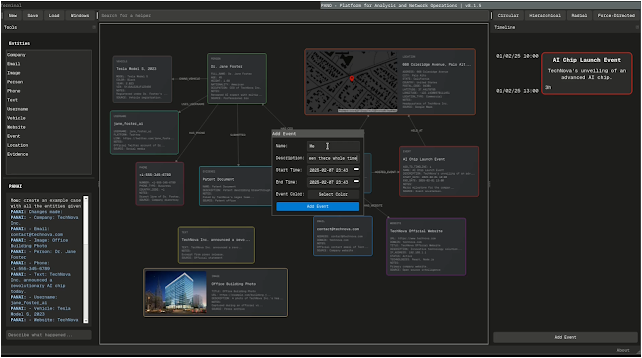
💡 Quick Start Guide
- Create Investigation: Start a new investigation or load an existing one
- Add Entities: Drag entities from the sidebar onto the graph
- Discover Connections: Use transforms to automatically find relationships
- Analyze: Use timeline and map views to understand patterns
- Save: Export your investigation for later use
🔍 Features
🕸️ Core Functionality
- Interactive Graph Visualization
- Drag-and-drop entity creation
- Multiple layout algorithms (Circular, Hierarchical, Radial, Force-Directed)
- Dynamic relationship mapping
-
Visual node and edge styling
-
Timeline Analysis
- Chronological event visualization
- Interactive timeline navigation
- Event filtering and grouping
-
Temporal relationship analysis
-
Map Integration
- Geographic data visualization
- Location-based analysis
- Interactive mapping features
- Coordinate plotting and tracking
🎯 Entity Management
- Supported Entity Types
- 📧 Email addresses
- 👤 Usernames
- 🌐 Websites
- 🖼️ Images
- 📍 Locations
- ⏰ Events
- 📝 Text content
- 🔧 Custom entity types
🔄 Transform System
- Email Analysis
- Google account investigation
- Calendar event extraction
- Location history analysis
-
Connected services discovery
-
Username Analysis
- Cross-platform username search
- Social media profile discovery
- Platform correlation
-
Web presence analysis
-
Image Analysis
- Reverse image search
- Visual content analysis
- Metadata extraction
- Related image discovery
🤖 AI Integration
- PANAI
- Natural language investigation assistant
- Automated entity extraction and relationship mapping
- Pattern recognition and anomaly detection
- Multi-language support
- Context-aware suggestions
- Timeline and graph analysis
🧩 Core Components
📦 Entities
Entities are the fundamental building blocks of PANO. They represent distinct pieces of information that can be connected and analyzed:
- Built-in Types
- 📧 Email: Email addresses with service detection
- 👤 Username: Social media and platform usernames
- 🌐 Website: Web pages with metadata
- 🖼️ Image: Images with EXIF and analysis
- 📍 Location: Geographic coordinates and addresses
- ⏰ Event: Time-based occurrences
-
📝 Text: Generic text content
-
Properties System
- Type-safe property validation
- Automatic property getters
- Dynamic property updates
- Custom property types
- Metadata support
⚡ Transforms
Transforms are automated operations that process entities to discover new information and relationships:
- Operation Types
- 🔍 Discovery: Find new entities from existing ones
- 🔗 Correlation: Connect related entities
- 📊 Analysis: Extract insights from entity data
- 🌐 OSINT: Gather open-source intelligence
-
🔄 Enrichment: Add data to existing entities
-
Features
- Async operation support
- Progress tracking
- Error handling
- Rate limiting
- Result validation
🛠️ Helpers
Helpers are specialized tools with dedicated UIs for specific investigation tasks:
- Available Helpers
- 🔍 Cross-Examination: Analyze statements and testimonies
- 👤 Portrait Creator: Generate facial composites
- 📸 Media Analyzer: Advanced image processing and analysis
- 🔍 Base Searcher: Search near places of interest
-
🔄 Translator: Translate text between languages
-
Helper Features
- Custom Qt interfaces
- Real-time updates
- Graph integration
- Data visualization
- Export capabilities
👥 Contributing
We welcome contributions! To contribute to PANO:
- Fork the repository at https://github.com/ALW1EZ/PANO/
- Make your changes in your fork
- Test your changes thoroughly
- Create a Pull Request to our main branch
- In your PR description, include:
- What the changes do
- Why you made these changes
- Any testing you’ve done
- Screenshots if applicable
Note: We use a single
mainbranch for development. All pull requests should be made directly tomain.
📖 Development Guide
Click to expand development documentation
### System Requirements – Operating System: Windows or Linux – Python 3.11+ – PySide6 for GUI – Internet connection for online features ### Custom Entities Entities are the core data structures in PANO. Each entity represents a piece of information with specific properties and behaviors. To create a custom entity: 1. Create a new file in the `entities` folder (e.g., `entities/phone_number.py`) 2. Implement your entity class:from dataclasses import dataclass
from typing import ClassVar, Dict, Any
from .base import Entity
@dataclass
class PhoneNumber(Entity):
name: ClassVar[str] = "Phone Number"
description: ClassVar[str] = "A phone number entity with country code and validation"
def init_properties(self):
"""Initialize phone number properties"""
self.setup_properties({
"number": str,
"country_code": str,
"carrier": str,
"type": str, # mobile, landline, etc.
"verified": bool
})
def update_label(self):
"""Update the display label"""
self.label = self.format_label(["country_code", "number"])
from dataclasses import dataclass
from typing import ClassVar, List
from .base import Transform
from entities.base import Entity
from entities.phone_number import PhoneNumber
from entities.location import Location
from ui.managers.status_manager import StatusManager
@dataclass
class PhoneLookup(Transform):
name: ClassVar[str] = "Phone Number Lookup"
description: ClassVar[str] = "Lookup phone number details and location"
input_types: ClassVar[List[str]] = ["PhoneNumber"]
output_types: ClassVar[List[str]] = ["Location"]
async def run(self, entity: PhoneNumber, graph) -> List[Entity]:
if not isinstance(entity, PhoneNumber):
return []
status = StatusManager.get()
operation_id = status.start_loading("Phone Lookup")
try:
# Your phone number lookup logic here
# Example: query an API for phone number details
location = Location(properties={
"country": "Example Country",
"region": "Example Region",
"carrier": "Example Carrier",
"source": "PhoneLookup transform"
})
return [location]
except Exception as e:
status.set_text(f"Error during phone lookup: {str(e)}")
return []
finally:
status.stop_loading(operation_id)
from PySide6.QtWidgets import (
QWidget, QVBoxLayout, QHBoxLayout, QPushButton,
QTextEdit, QLabel, QComboBox
)
from .base import BaseHelper
from qasync import asyncSlot
class DummyHelper(BaseHelper):
"""A dummy helper for testing"""
name = "Dummy Helper"
description = "A dummy helper for testing"
def setup_ui(self):
"""Initialize the helper's user interface"""
# Create input text area
self.input_label = QLabel("Input:")
self.input_text = QTextEdit()
self.input_text.setPlaceholderText("Enter text to process...")
self.input_text.setMinimumHeight(100)
# Create operation selector
operation_layout = QHBoxLayout()
self.operation_label = QLabel("Operation:")
self.operation_combo = QComboBox()
self.operation_combo.addItems(["Uppercase", "Lowercase", "Title Case"])
operation_layout.addWidget(self.operation_label)
operation_layout.addWidget(self.operation_combo)
# Create process button
self.process_btn = QPushButton("Process")
self.process_btn.clicked.connect(self.process_text)
# Create output text area
self.output_label = QLabel("Output:")
self.output_text = QTextEdit()
self.output_text.setReadOnly(True)
self.output_text.setMinimumHeight(100)
# Add widgets to main layout
self.main_layout.addWidget(self.input_label)
self.main_layout.addWidget(self.input_text)
self.main_layout.addLayout(operation_layout)
self.main_layout.addWidget(self.process_btn)
self.main_layout.addWidget(self.output_label)
self.main_layout.addWidget(self.output_text)
# Set dialog size
self.resize(400, 500)
@asyncSlot()
async def process_text(self):
"""Process the input text based on selected operation"""
text = self.input_text.toPlainText()
operation = self.operation_combo.currentText()
if operation == "Uppercase":
result = text.upper()
elif operation == "Lowercase":
result = text.lower()
else: # Title Case
result = text.title()
self.output_text.setPlainText(result)
📄 License
This project is licensed under the Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial (CC BY-NC) License.
You are free to: – ✅ Share: Copy and redistribute the material – ✅ Adapt: Remix, transform, and build upon the material
Under these terms: – ℹ️ Attribution: You must give appropriate credit – 🚫 NonCommercial: No commercial use – 🔓 No additional restrictions
🙏 Acknowledgments
Special thanks to all library authors and contributors who made this project possible.
👨💻 Author
Created by ALW1EZ with AI ❤️
Original Source: kitploit.com
A considerable amount of time and effort goes into maintaining this website, creating backend automation and creating new features and content for you to make actionable intelligence decisions. Everyone that supports the site helps enable new functionality.
If you like the site, please support us on “Patreon” or “Buy Me A Coffee” using the buttons below
To keep up to date follow us on the below channels.

![[Palo Alto Networks Security Advisories] PAN-SA-2025-0016 Chromium: Monthly Vulnerability Update (October 2025) 2 Palo_Alto_Networks_Logo](https://www.redpacketsecurity.com/wp-content/uploads/2025/02/Palo_Alto_Networks_Logo-300x55.png)

