Ransomware: February 2022 review
The Malwarebytes Threat Intelligence team continuously monitors the threat landscape to stay on top of existing and emerging attacks. In this February 2022 ransomware review, we go over some the most successful ransomware incidents based on both open source and dark web intelligence.
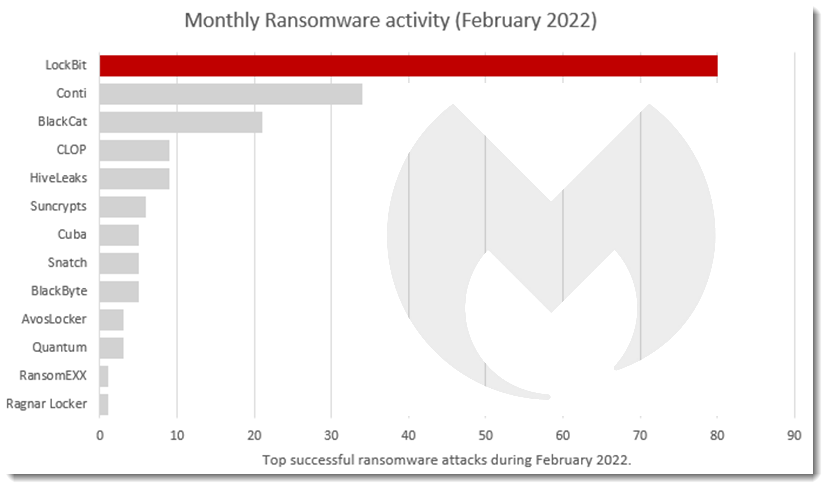
BlackByte
- Observed since:
July 2021 - Ransomware note:
BlackByteRestore.txt - Ransomware extension:
.BlackByte - Kill Chain: Some victims reported that attackers used known
Microsoft Exchange Servervulnerabilities to gain access to their networks. >BlackByte Ransomware - Sample hash:
1df11bc19aa52b623bdf15380e3fded56d8eb6fb7b53a2240779864b1a6474ad
HermeticRansom (PartyTicket)
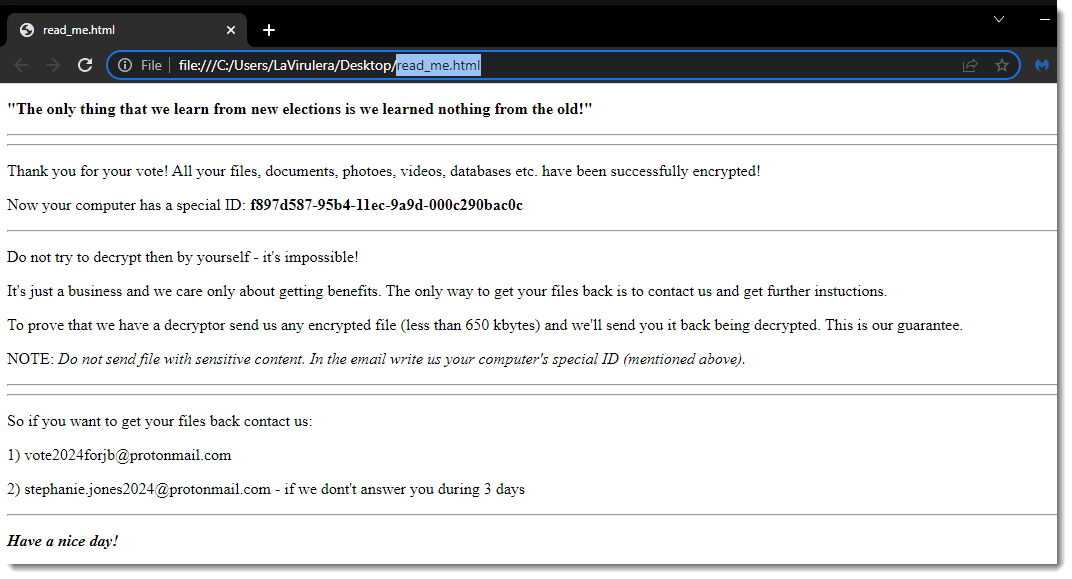
- Observed since:
February 2022 - Ransomware note:
read_me.html - Ransomware extension:
<original file name>.[vote2024forjb@protonmail[.]com].encryptedJB - Kill Chain: On Feb. 23, 2022, destructive attacks were conducted against Ukrainian entities. Industry reporting has claimed the Go-based ransomware dubbed PartyTicket (or HermeticRansom) was identified at several organizations affected by the attack
- Sample hash:
4dc13bb83a16d4ff9865a51b3e4d24112327c526c1392e14d56f20d6f4eaf382
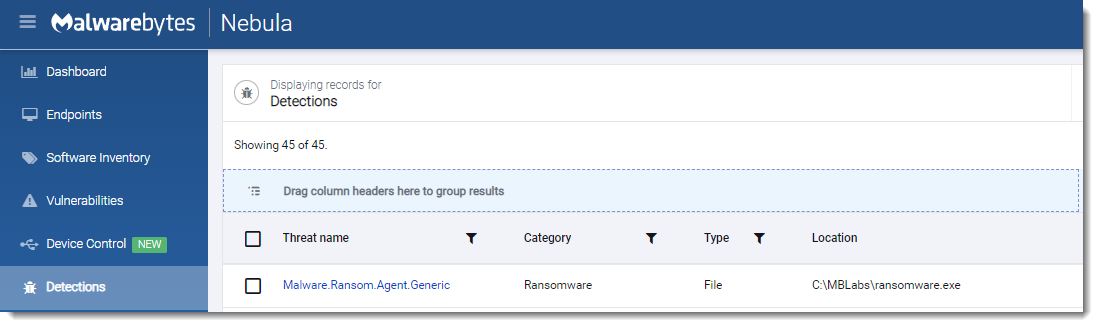
SFile (Escal)
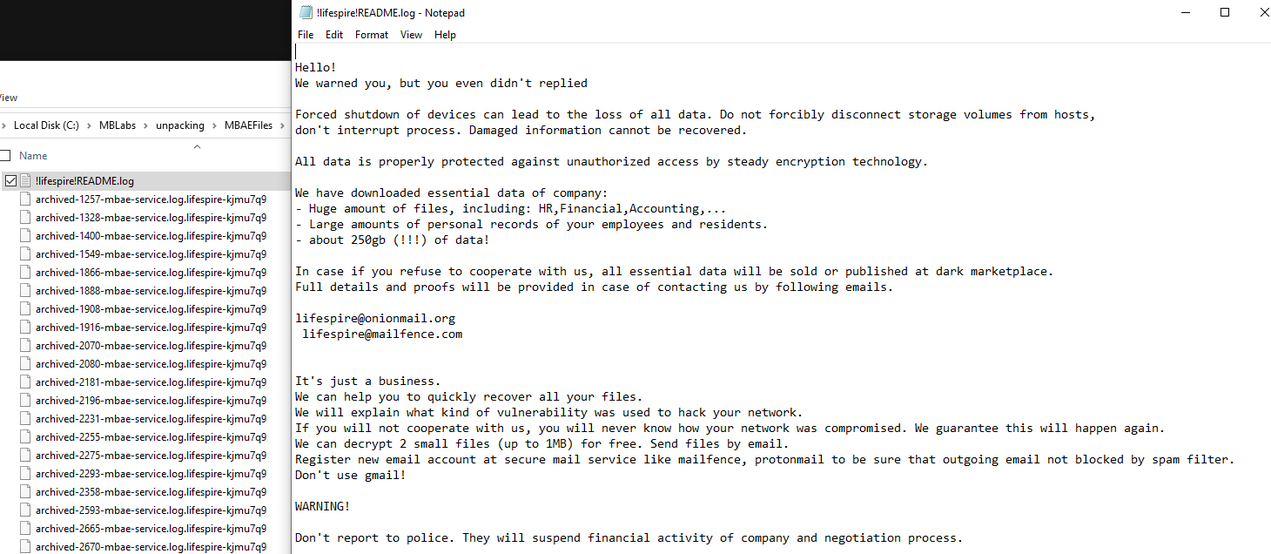
- Observed since:
February 2022 - Ransomware note:
.<company_name>.!README.log - Ransomware extension:
.<company_name>.<random> - Kill Chain: Smaller ransomware strains used in targeted attacks
- Sample hash:
6a7cef95a501cce16dce6f5a645fc97c4bcbb568c83dde5a7f2e4a0d7555dd98
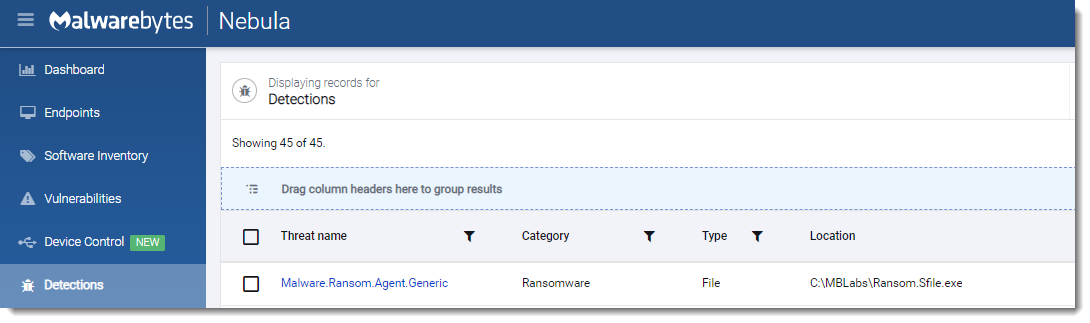
LockBit 2.0
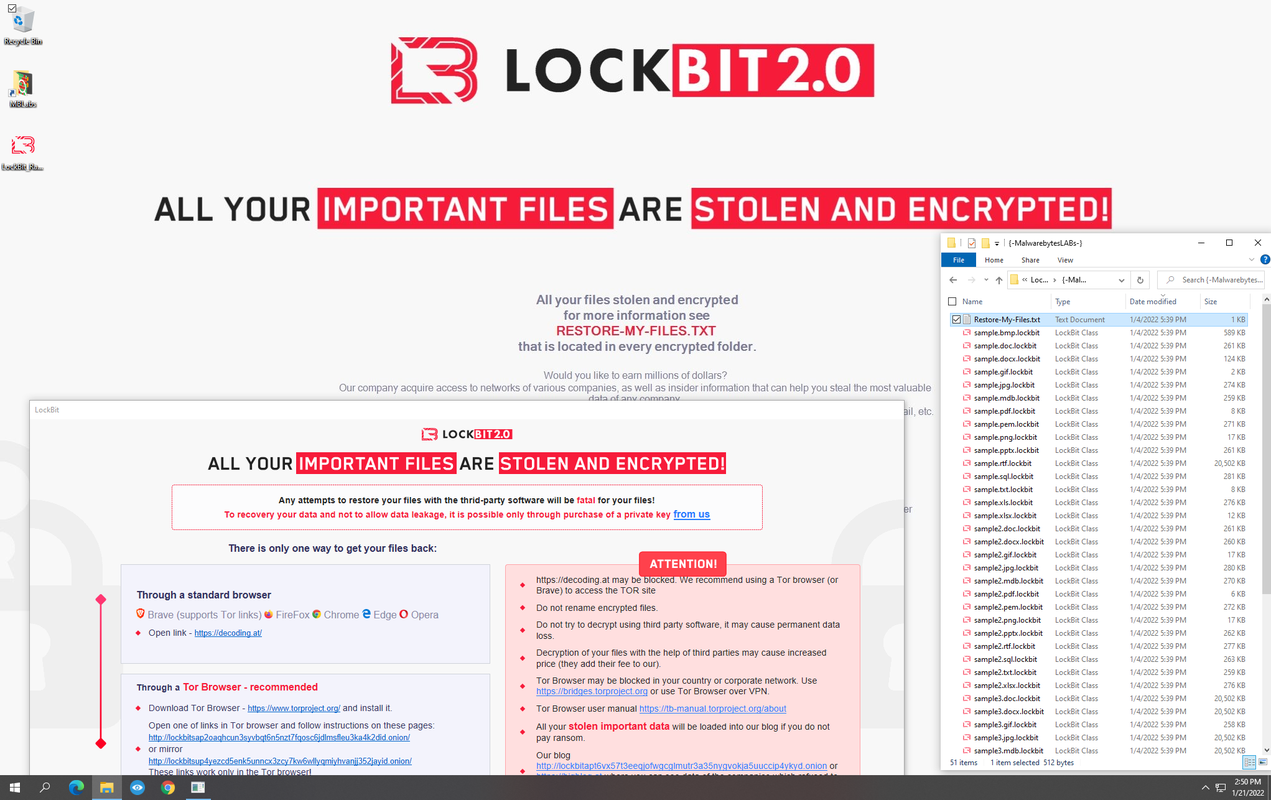
- Observed since:
September 2019 - Ransomware note:
Restore-My-Files.txt - Ransomware extension:
.lockbit - Kill Chain:
Brute force attack on a web server containing an outdated VPN service>LockBit - Sample hash:
9feed0c7fa8c1d32390e1c168051267df61f11b048ec62aa5b8e66f60e8083af
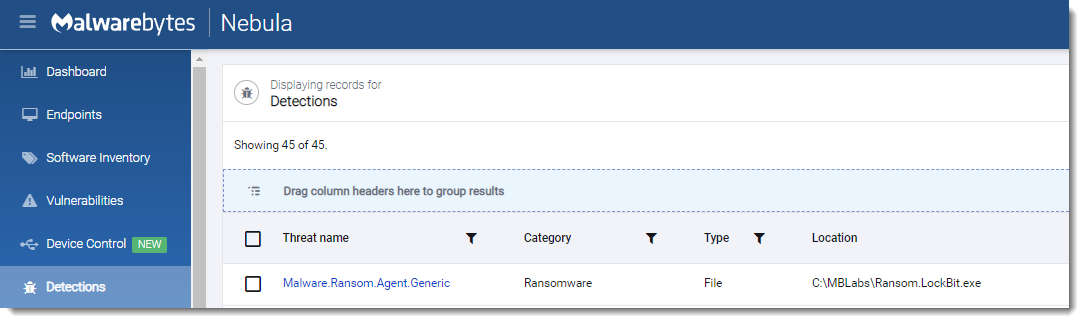
Magniber
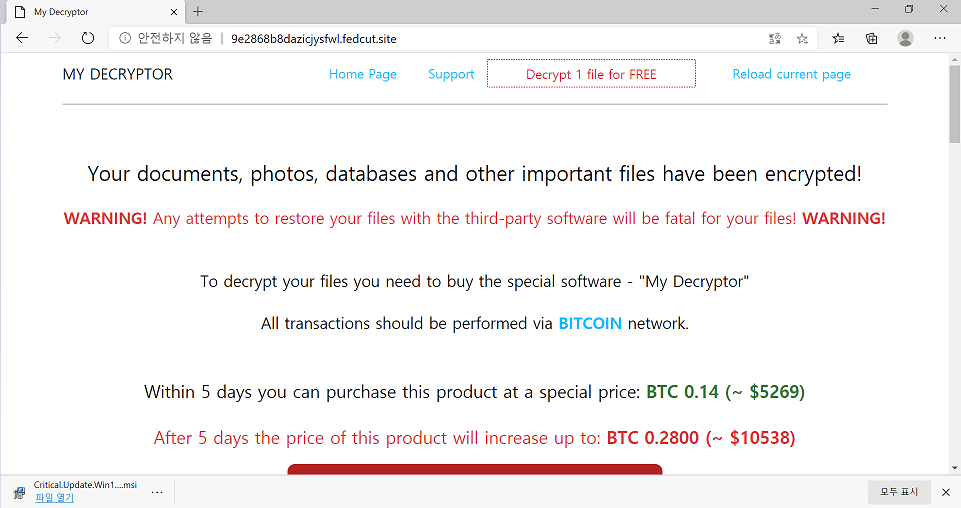
- Observed since:
October 2017 - Ransomware note:
readme.txt - Ransomware extension:
dihlxbl - Kill Chain: Being Distributed via Microsoft Edge and Google Chrome (Korean users)
- Sample hash:
06ea8f2b8b70b665cbecab797125733f75014052d710515c5ca2d908f3852349
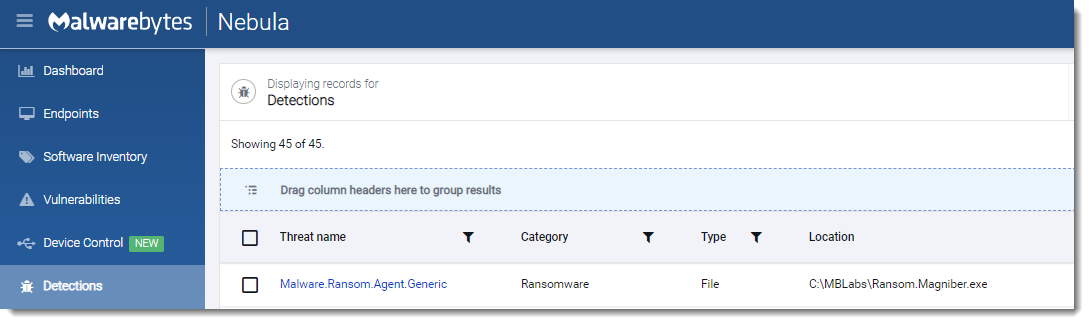
Surtr
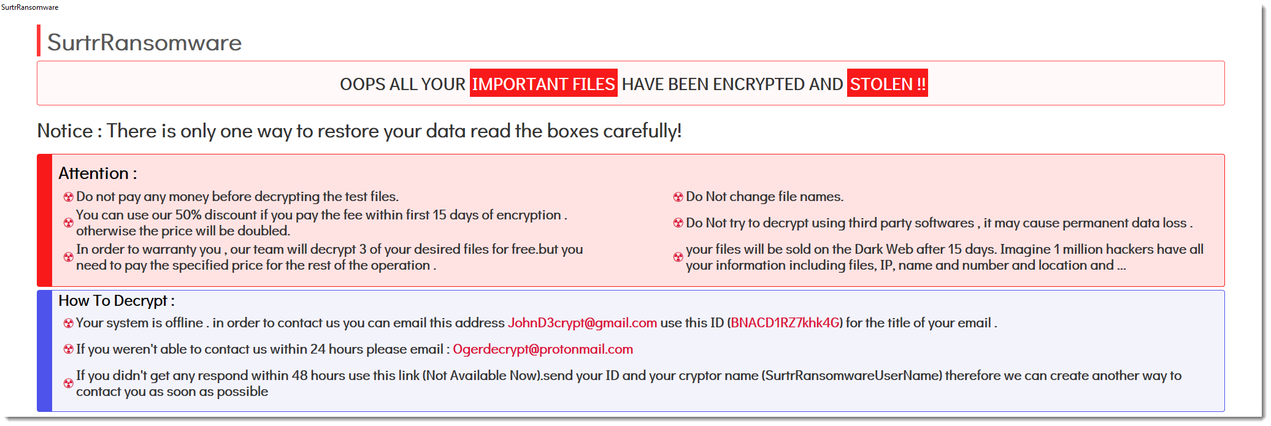
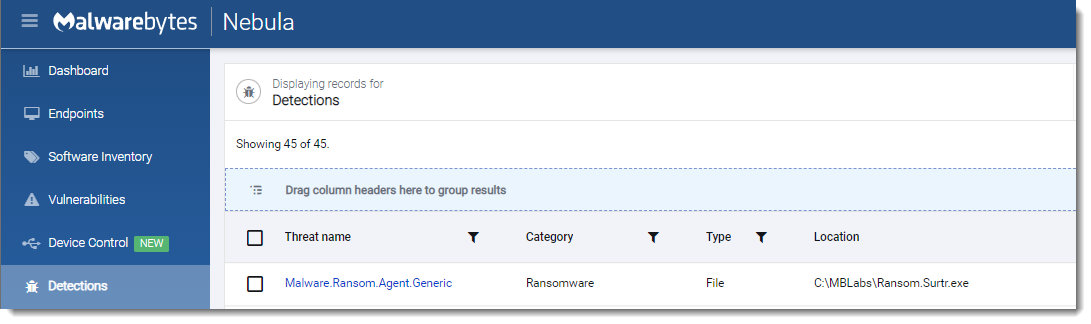
- Observed since:
December 2021 - Ransomware note:
SURTR_README.hta - Ransomware extension:
.surtr - Kill Chain:
Spear-Phishing>MalDoc>Surtr Ransomware - Sample hash:
40e5bb0526169c02126ffa60a09041e5e5453a24b26bc837036748b150fa3fae
Sugar
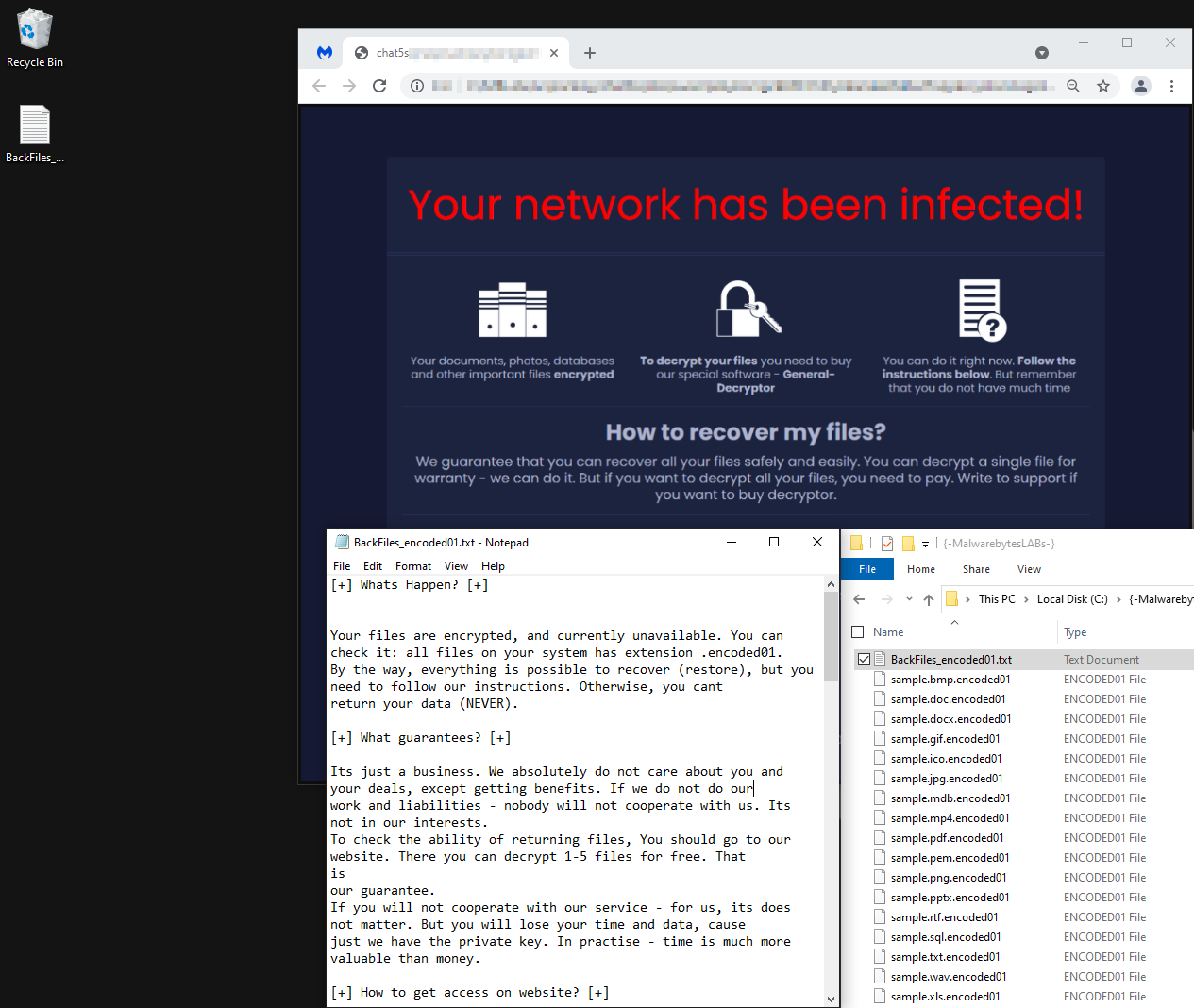
- Observed since:
January 2021 - Ransomware note:
BackFiles_encoded01.txt - Ransomware extension:
.Encoded01 - Kill Chain:
Spear-Phishing>MalDoc>Sugar Ransomware - Sample hash:
4a97bc8111631795cb730dfe7836d0afac3131ed8a91db81dde5062bb8021058
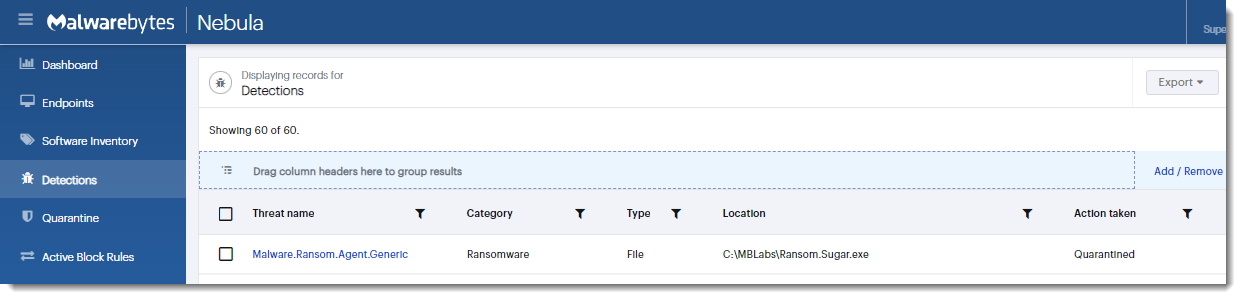
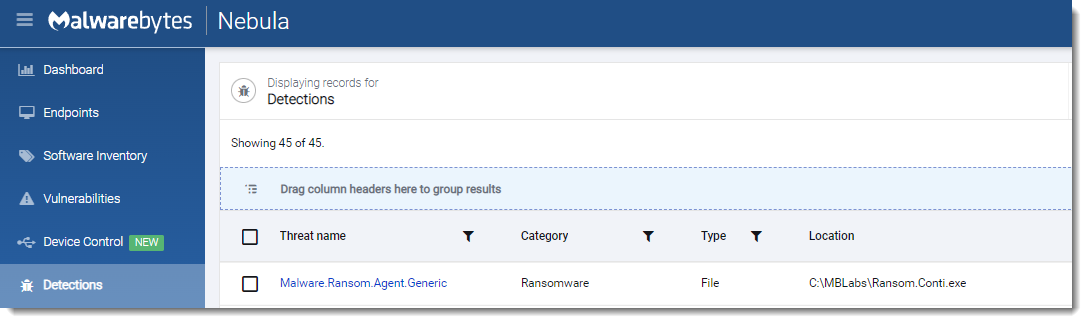
Conti
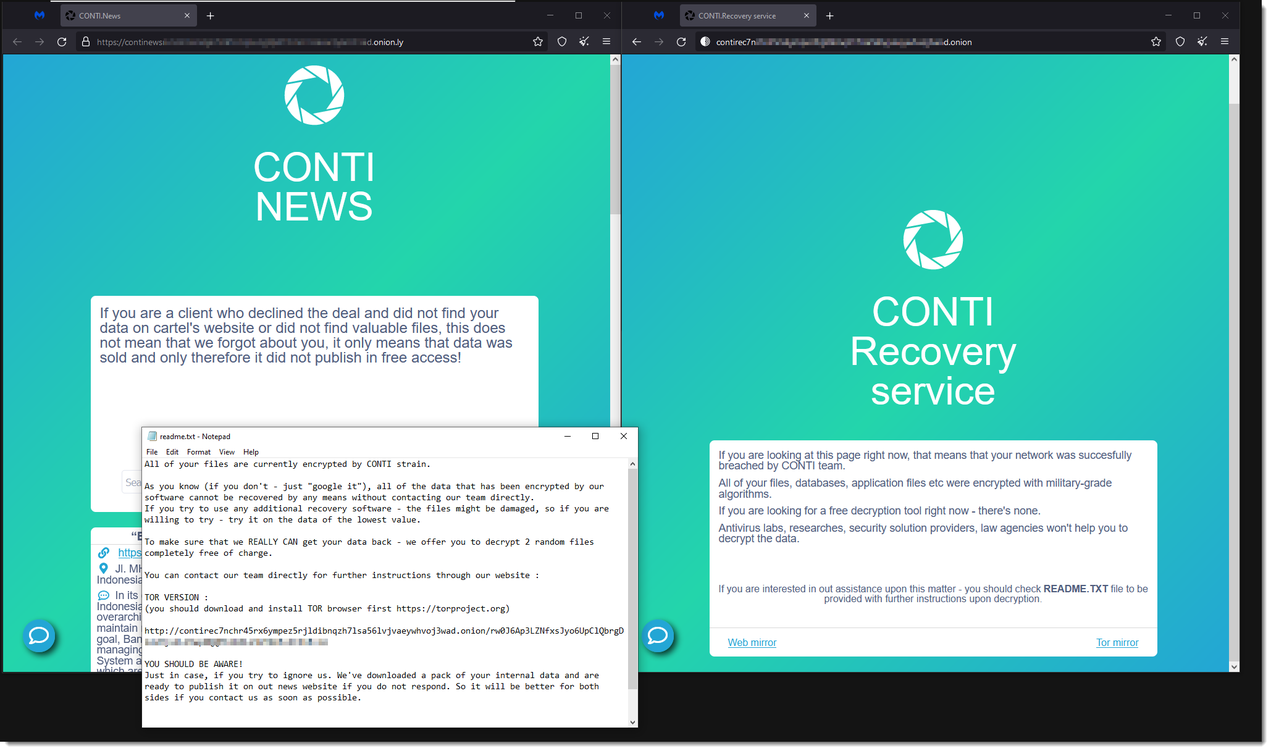
- Observed since:
June 2021 - Ransomware ext:
.CONTI - Ransomware notes:
CONTI.txt–R3ADM3.txt–readme.txt–CONTI_README.txt - Kill Chain:
Spear-Phishing>Bazar backdoor, orIcedID>Cobalt Strike>Conti Ransomware - Sample hash:
24ac73821de77cc9644d2ac40e97067ff63f625b5f20e085ad10535e47d7db59
Mitigations
Source: IC3.gov
- Implement regular backups of all data to be stored as air-gapped, password-protected copies offline. Ensure these copies are not accessible for modification or deletion from any system where the original data resides.
- Implement network segmentation, such that all machines on your network are not accessible from every other machine.
- Install and regularly update antivirus software on all hosts, and enable real-time detection.
- Install updates/patch operating systems, software, and firmware as soon as updates/patches are released.
- Review domain controllers, servers, workstations, and active directories for new or unrecognized user accounts.
- Audit user accounts with administrative privileges and configures access controls with the least privilege in mind. Do not give all users administrative privileges.
- Disable unused remote access/Remote Desktop Protocol (RDP) ports and monitor remote access/RDP logs for any unusual activity.
- Consider adding an email banner to emails received from outside your organization.
- Disable hyperlinks in received emails.
- Use double authentication when logging into accounts or services.
- Ensure routine auditing is conducted for all accounts.
- Ensure all the identified IOCs are input into the network SIEM for continuous monitoring and alerts.
How Malwarebytes protects against ransomware
Malwarebytes can protect systems against all ransomware variants in several ways.
The Malwarebytes Anti-Malware technology detects malicious files, browser modifications, and system modifications on Windows PCs using a combination of signature-based and signatureless technologies. This layer of protection detects the Ransomware binary itself. Detections can happen in real-time as the binary is run or the infection can be rooted out from an already-compromised machine by conducting a full system scan.
Anti-Ransomware is a signatureless technology in charge of monitoring system activity of processes against a certain subset of data in specific locations on the endpoint. Using patented technology, Anti-Ransomware assesses changes in those data files. If an internal scoring threshold is crossed by a monitored process, it triggers a detection from the Anti-Ransomware component.
For those already infected, Ransomware Rollback can help recover encrypted files within 72 hours of the attack. Rollback creates a local cache on the endpoint to store changes to files on the system. It can use this cache to help revert changes caused by a threat. The Rollback feature is dependent on activity monitoring available in Malwarebytes Endpoint Detection and Response.
Recommended reading: How to protect your RDP access from ransomware attacks
The post Ransomware: February 2022 review appeared first on Malwarebytes Labs.
If you like the site, please consider joining the telegram channel or supporting us on Patreon using the button below.


![Cobalt Strike Beacon Detected - 101[.]200[.]76[.]102:80 19 Cobalt-Strike](https://www.redpacketsecurity.com/wp-content/uploads/2021/11/Cobalt-Strike-300x201.jpg)